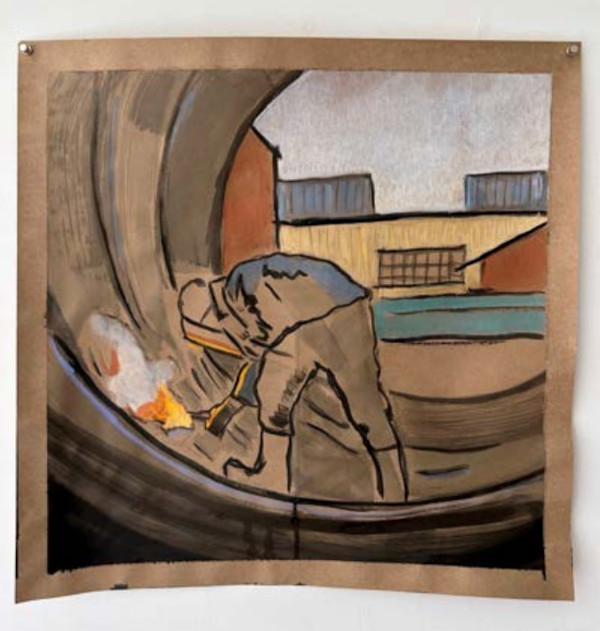
An ingot is a large, solid block of metal that has been cast from molten steel into a mold, allowing it to be later reheated and shaped into usable forms, such as plates, bars, or rails. In early steel production, newly cast steel ingots were transported by small industrial locomotives to the next phase of processing.
Before the introduction of continuous casting, molten steel was poured into heavy molds that were loaded onto specialized flatcars known as ingot buggies. These trains carried the glowing ingots from the casting floor to the stripper shed, where molds were removed, and then to soaking pits for reheating before rolling.
- Collections: Cory Bonnet